A limit is a value that a function or sequence approaches when the input (for functions) or index (for sequences) gets closer to a specific value. It helps us understand how a function approaches a certain point or value without actually reaching it.
Limits are an essential part of calculus and play a crucial role in understanding derivatives and integrals. This article will explore the definition of limits with their different types. For a better understanding, different examples will be covered in the examples section.

Table of Contents Show
Definition of Limit
Let f(x) be a function defined in an open interval containing the number c (need not be at c). The limit of f(x) as x approaches c is L if, for every ε > 0, there exists a positive number δ such that for all x in the domain of f. If 0 < |x – c| < δ, then |f(x) – L| < ε.
In other words; the limit of f(x) as x approaches c is the number that f(x) gets closer and closer to as x gets closer and closer to c. The limit of a function as x approaches a can be denoted symbolically as:
lim x → c f(x) = L
Here,
- The ‘lim’ expresses the limit.
- x is the variable that approaches a specific value.
- c denotes the value that x is approaching.
- f(x) is the function whose behavior we are studying.
- L is the value that the function f(x) approaches as x gets closer and closer to a.
Classification of Limit
Limits in mathematics can be classified into several categories based on their properties and behavior. Here are the main types of limits:
- One-Sided Limits
One-sided limits focus on approaching a value from a particular direction. We have two types:
Left-hand Limit
This represents the limit as we approach from the left side of point c. Symbolically, it is denoted as:
lim x → c– f (x)
Right-hand Limit
The right-hand limit approaches from the right side of c.
lim x → c+ f (x)
- Two-Sided Limits
A two-sided limit considers the behavior of a function as it approaches a particular point from both directions to determine its overall limit at that point.
- Infinite Limits
An infinite limit occurs when a function approaches either positive or negative infinity. This can be expressed as lim x → c f (x) = ±∞.
- Limits at Infinity
Limits at infinity deal with the behavior of a function as the variable moves towards positive or negative infinity. Mathematically, lim x → ±∞ f(x) = L, where L is a finite number.
Properties and Rules of Limit
Here is a table summarizing some key properties and rules of limits in calculus:
| Property/Rule Name | Mathematics Form |
| Constant Rule | lim x→c k = k for any constant k. |
| Limit of a Sum/Difference | lim x→c [f(x) ± g(x)] = lim x→c f(x) ± lim x→c g(x) |
| Limit of a Product | lim x→ c [f(x) . g(x)] = lim x→ c f(x) . lim x→ c g(x) |
| Limit of a Quotient | lim x→ c (f(x) / g(x)) = lim x→ c f(x) / lim x→ c g(x) (lim x→ c g(x) ≠ 0) |
| Limit of a Constant Multiple | lim x→ c [k f(x)] = k lim x→ c f(x) for any constant k. |
| Limit of a Power Function | lim x→ c (f(x)) k = (lim x→ c f(x)) k for any integer k. |
| Limit of a Root Function | lim x→ c √ (f(x)) = √ (lim x→ c (f(x))) |
| Limit of an Exponential | lim x→ c ef(x) = e lim x→ c f(x) |
| Limit of a Logarithm | lim x→ c ln(f(x)) =ln(lim x→ c f(x)), provided lim x→ c f(x) > 0 |
How to Find Limit?
Here is how you can find the limit of a function:
Finding limit by Direct Substitution:
The value c can be substituted directly into the function. There is a limit if the result is a well-defined number.
Simplify:
Direct substitution sometimes does not work because it leads to an indeterminate form like 0/0 or ∞/∞. In such cases, try to simplify the expression by factoring, canceling common factors, or using algebraic techniques.
L’Hôpital’s Rule:
You can apply L’Hôpital’s Rule if direct substitution and simplification do not work and you end up with an indeterminate form. This rule allows you to take the derivative of both the numerator and denominator repeatedly until you get a determinate form.
Special Limits:
Some limits have well-known values. Be familiar with these special limits.
- lim x→ 0 ((1 – cos x)/ x) = 1
- lim x→ 0 (Sin x / x) = 1
- lim x→ 0 (1 + x) (1/x) = e
- lim x→ 0 (xn – an)/ (x – a) = na(n – 1)
Examples of Limits with their Solution
Here are some examples of limits along with their solutions:
Example 1:
Find the limit of the function f(x) = 2x + 3 as x approaches 4.
Solution:
Simply substitute x = 4 into the function:
f(4) = 2(4) + 3
= 8 + 3
= 11
Thus, lim x→ 4 (2x + 3) = 11.
Example 2:
Evaluate lim x→1 (x – 1) / (x2 – 1)
Solution:
If we directly substitute x = 1, we get an indeterminate form 0/0, which means we need to simplify. We can factor the denominator:
= lim x→1 (x – 1) / (x – 1) (x + 1)
Now, we can cancel out the common factor of (x + 1):
= lim x→1 (1/(x + 1))
Now, we can substitute x = 1:
lim x→1 (1/(x + 1))= 1/(1 + 1)
= 1/2
Hence, lim x→1 (x – 1) / (x2 – 1) = 1/2
Example 3:
Find the limit of the function h(x) = sin(x)/x as x approaches 0.
Solution:
This is a well-known limit. Direct substitution gives us an indeterminate form, 0/0.
We can use L’Hôpital’s Rule here. Take the derivatives of the numerator and denominator:
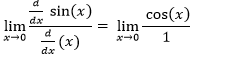
= cos (0)/1
= 1/1 = 1
The limit of the function h(x) as x approaches 0 is 1.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the fundamental concept of limits in calculus. We have defined limits mathematically and classified them into various types. We have discussed essential properties and several methods to find limits effectively.
Finally, we provided concrete examples of limit calculations to illustrate the concepts discussed. These examples demonstrate how to apply the principles of limits to evaluate specific functions, even when faced with challenging cases.
